管用时间:2023-7.9-2023.7.16
由于有动物学实习,不知道能做多少。
本期主要刷 cf1600-2000 的题目来康复,期望能 div2 做出来
20230711
CF1844A
输出 A+B 即可
CF1844B
把 1 放在最中间,2,3 放在最边上即可。
CF1844C
由于可以去除两端而无影响,直接一个 dp 就可以了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int maxn=200200;
const int looker=-1e18;
int n,T,f[maxn],ans,a[maxn];
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i];
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++) f[i]=looker;
ans=looker;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
f[i]=max(f[max(i-2,0ll)]+a[i],max(f[max(i-2,0ll)],a[i]));
ans=max(ans,f[i]);
}
cout<<ans<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}
|
CF1844D
考虑 n 分解质因数为 x∗y 的意义,一定表示第 i 和第 i+x,i+y 不能相同颜色,直接从2开始试除,除不动的时候就可以是原来的数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define lowbit(x) (x&(-x))
using namespace std;
const int maxn=500200;
int n,m,q,a[maxn];
int rk[maxn],cnt,kr[maxn];
int c[maxn];
int tot1,mmx;
void add_tree(int x,int y)
{
while(x<=n)
{
c[x]+=y;
x+=lowbit(x);
}
}
int query_tree(int x)
{
int ans=0;
while(x)
{
ans+=c[x];
x-=lowbit(x);
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin>>n>>m>>q;
set <int> looker;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
char t;
cin>>t;
a[i]=t-'0';
}
int t1,t2;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) looker.insert(i);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
cin>>t1>>t2;
for(auto it =looker.lower_bound(t1);it!=looker.end()&&*it<=t2;it=looker.erase(it))
{
rk[*it]=++cnt;
kr[cnt]=*it;
}
}
mmx=cnt;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!rk[i]) rk[i]=++cnt,kr[cnt]=i;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(a[kr[i]])
{
tot1++;
add_tree(i,1);
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=q;i++)
{
int tmp;
cin>>tmp;
if(a[tmp]) tot1--;
else tot1++;
a[tmp]^=1;
add_tree(rk[tmp],a[tmp]?1:-1);
cout<<min(mmx,tot1)-query_tree(min(mmx,tot1))<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}
|
20230712
CF1847D
给你一个 01 串,我们用他的某些子串拼成串 T ,你可以交换原来的串的 0 和 1,为了让 T 字典序最大,你至少要交换多少次?
我们很显然有个贪心是先满足前面的串全 1 ,这个时候我们可以定义某个位置的优先度,由于是从做到右,我们可以从左到右赋予它优先度。这里可以用一个 set 来做。
然后就假设我们当前有 x 个 1,那么我们一定是把这 x 个 1 给优先度为前 x 的个数的东西。用一个树状数组来做就好了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define lowbit(x) (x&(-x))
using namespace std;
const int maxn=500200;
int n,m,q,a[maxn];
int rk[maxn],cnt,kr[maxn];
int c[maxn];
int tot1,mmx;
void add_tree(int x,int y)
{
while(x<=n)
{
c[x]+=y;
x+=lowbit(x);
}
}
int query_tree(int x)
{
int ans=0;
while(x)
{
ans+=c[x];
x-=lowbit(x);
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin>>n>>m>>q;
set <int> looker;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
char t;
cin>>t;
a[i]=t-'0';
}
int t1,t2;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) looker.insert(i);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
cin>>t1>>t2;
for(auto it =looker.lower_bound(t1);it!=looker.end()&&*it<=t2;it=looker.erase(it))
{
rk[*it]=++cnt;
kr[cnt]=*it;
}
}
mmx=cnt;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!rk[i]) rk[i]=++cnt,kr[cnt]=i;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(a[kr[i]])
{
tot1++;
add_tree(i,1);
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=q;i++)
{
int tmp;
cin>>tmp;
if(a[tmp]) tot1--;
else tot1++;
a[tmp]^=1;
add_tree(rk[tmp],a[tmp]?1:-1);
cout<<min(mmx,tot1)-query_tree(min(mmx,tot1))<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}
|
20230713
CF1844E. Great Grids
每个 2*2 方格有三种字母,并且保证相邻的不相同,现在限制某些格子对之间必须相同,询问是否存在这个合法的 n*m 的方格。
其实画图就可以发现,如果是要求对角相同,这个 2*2 的格子一定只有这4种情况( a,b,c 分别代表模 3 意义下的 0,1,2).
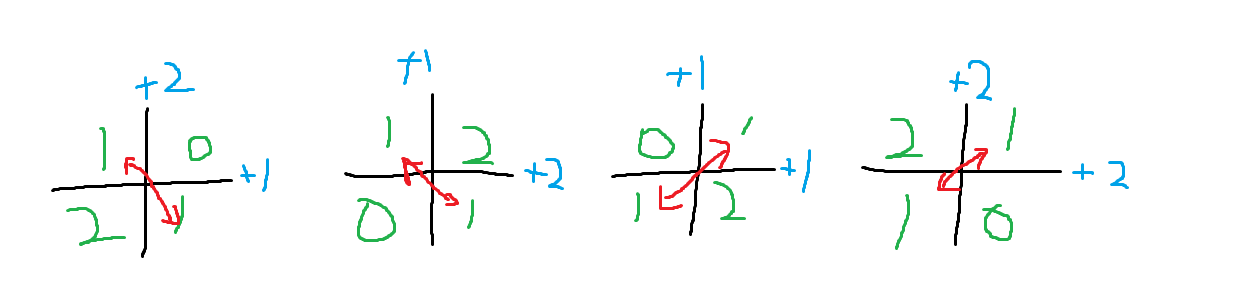
此刻考虑把这个中心竖轴和横轴抽象为四个点,r1,r2,c1,c2 。分别代表列 +1,+2 行 +1,+2 ,对于有这种要求对角线要求的格子,如图所示,对于左上=右下,连 r2->c1,r1->c2 对于右上=左下,连 r1->c1,r2->c2 。 一旦 r1,r2 或者 c1,c2 在一个并查集了,说明不可能存在这个方格。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=10010;
int n,m,q,f[maxn],T;
int getf(int x)
{
if(f[x]==x) return x;
return f[x]=getf(f[x]);
}
void merge(int x,int y)
{
x=getf(f[x]);
y=getf(f[y]);
f[x]=y;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
cin>>n>>m>>q;
for(int i=1;i<=n*2+m*2;i++) f[i]=i;
for(int i=1;i<=q;i++)
{
int t1,t2,t3,t4;
cin>>t1>>t2>>t3>>t4;
if(t1>t3)
{
swap(t1,t3);
swap(t2,t4);
}
if(t2<t4)
{
merge(t1,t2+n*2+m);
merge(t1+n,t2+n*2);
}
else
{
merge(t1,t4+n*2);
merge(t1+n,t4+n*2+m);
}
}
int bj=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(getf(i)==getf(i+n))
{
cout<<"NO\n";
bj=1;
break;
}
}
if(bj) continue;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
if(getf(i+n*2)==getf(i+n*2+m))
{
cout<<"NO\n";
bj=1;
break;
}
}
if(bj) continue;
cout<<"YES\n";
}
}
|
20230714
CF1844F1
给你一个数组 a ,对其任意排序得到数组 b ,试着最小化 S=i=1∑n−1∣bi+1−bi−c∣ ,同时满足 b 字典序最小。
显然对于 c≥0 的情况,从小到大排序即可。
对于 c<0 情况,可以保证从大到小一定是最优的。
例如,我们现在有 x>y>z ,我们取两个排布,例如 xyz,xzy,写出它们的s1=∣y−x−c∣+∣z−y−c∣,s2=∣z−x−c∣+∣y−z−c∣ ,由于z−x=z−y+y−z ,代入原式则有 s2=∣y−x−c+(z−y)∣+∣y−z−c∣ 由于 z<y ,一定有 (z−y)−c<−c , 也就是 s1<s2 ,同理可以推出其他情况。
证明他是最优的,我们接下来就是找字典序最小的,这个简单贪心就能做了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int maxn=5050;
const int looker=-1e18;
int n,T,f[maxn],ans,a[maxn],b[maxn];
int c;
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
cin>>n>>c;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i];
if(c<0) sort(a+1,a+n+1,greater<int>());
else sort(a+1,a+n+1);
if(c>=0)
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cout<<a[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
continue;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=n;j>i;j--)
{
int bascost=0,nowcost=0;
if(j<n) bascost+=abs(a[j+1]-a[j]-c);
bascost+=abs(a[j]-a[j-1]-c);
if(i>1) bascost+=abs(a[i]-a[i-1]-c);
nowcost+=abs(a[i]-a[j]-c);
if(i>1)nowcost+=abs(a[j]-a[i-1]-c);
if(j<n) nowcost+=abs(a[j+1]-a[j-1]-c);
if(bascost==nowcost)
for(;j>=i+1;j--) swap(a[j],a[j-1]);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cout<<a[i]<<' ';
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
20230715
1845D - Rating System
题目大意:给你一段差分序列,当序列前缀和大于等于 k 时候,后面数不会低于 k ,试求出 k 使得序列最后一位最大。
显然要达到了才能 k 才有意义,把序列分成两段,前一段前缀和大于k,右边另外考虑,比如右边是序列 −100,2,4,−5,3,1 ,我们设 g(x)>0 表示 [x,n] 能够增加的个数。
我们从后向前推,g(x)=[5,5,4,4,4,1] 显然,这个可以用一个栈结构来维护,栈底(特判小于 0 情况)即g(x)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define lowbit(x) (x&(-x))
using namespace std;
const int maxn=300200;
int n,a[maxn],s[maxn],c[maxn],T,ans,ansk;
int st[maxn],top,g[maxn];
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
s[i]=s[i-1]+a[i];
c[i]=0;
}
ans=0,ansk=0;
top=0;
for(int i=n;i;i--)
{
st[++top]=a[i];
while(top>1&&st[top]+st[top-1]>0&&st[top]>0)
{
st[top-1]+=st[top];
top--;
}
g[i]=max(st[1],0ll);
if(ans<s[i-1]+g[i])
{
ans=s[i-1]+g[i];
ansk=s[i-1];
}
}
cout<<ansk<<'\n';
}
}
|
CF1842D. Tenzing and His Animal Friends